Exploring Capillary Tube Thermal Mass Flow Meters & Controllers
Abstract
This article delves into the realm of Capillary Tube Thermal Mass Flow Meters & Controllers. They are common tools in industrial and laboratory applications, as well as the semiconductor industry. Driven by the desire to demystify these instruments, this blog, sheds light on their working principles, applications, and best practices. We explore their historical evolution, emphasizing their pivotal role in various industries. Additionally, we discuss the advantages of direct mass flow rate measurement and compare thermal mass flow meters with other types.


Introduction
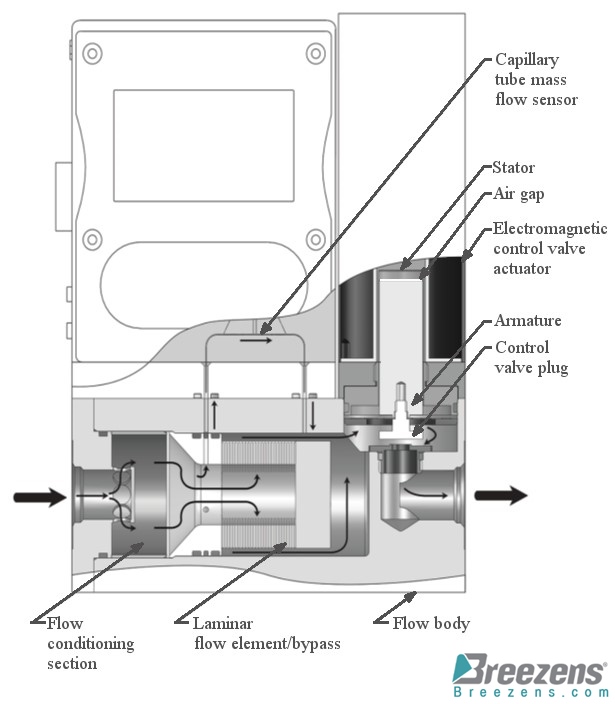
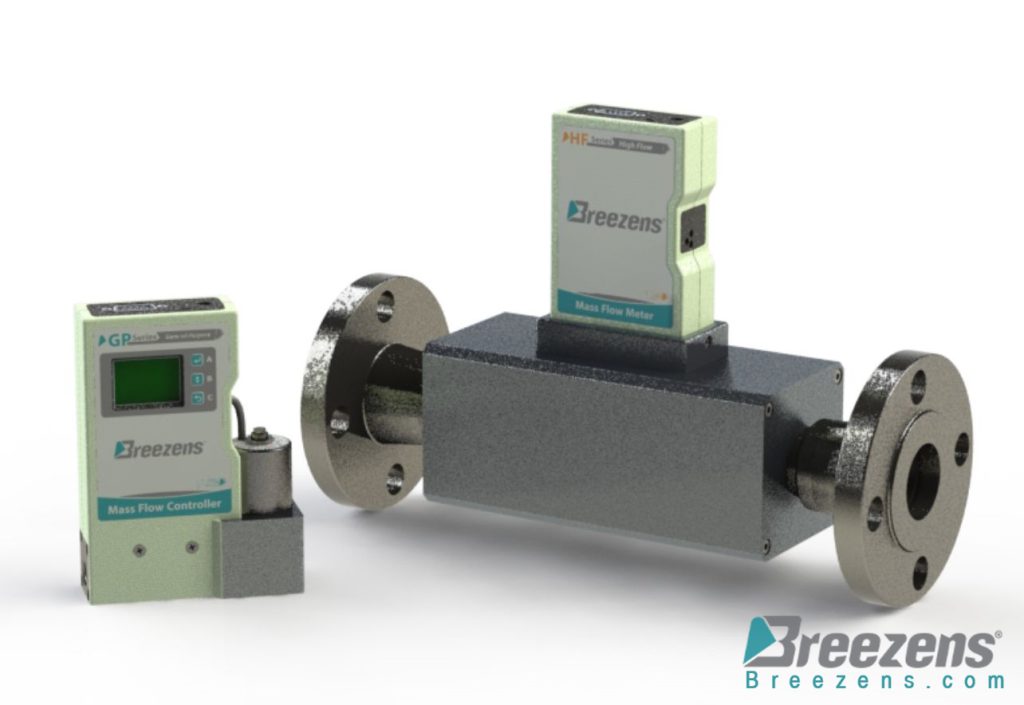
Capillary tube thermal mass flow meters directly measure the mass flow rate of clean gases in lower ranges. The addition of a flow control valve to the flow body creates a capillary tube thermal mass flow controller. It is not only monitors but also adjusts the mass flow rate to a user-selected set-point value.
Historical Perspective
Commercialized in the 1960s, thermal mass flow meters initially found use in the space industry and semiconductor device fabrication. As the semiconductor industry grew, so did the demand for these flow controllers. In the 1970s and 1980s, various industries recognized their benefits, leading to the formation of new companies to meet market needs. Thermal instruments remain popular due to their accuracy, compactness, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Primary Advantage
The key advantage lies in the direct measurement of mass flow rate, distinguishing capillary tube thermal instruments from those measuring volumetric flow rate. This distinction is crucial as most industries aim to measure and control the mass of gas entering their processes.


Types of Direct Mass Flow Meters
Two main types exist: Coriolis mass flow meters and thermal mass flow meters. Coriolis meters work with both liquids and gases, offering high accuracy and pressure drop but are relatively expensive. Thermal mass flow meters, on the other hand, measure gases’ mass flow rate, providing medium to high accuracy, low pressure drops, and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for gas-related applications.
Applications of Capillary Tube Thermal Mass Flow Meters and Controllers
These instruments find broad applications in general industrial and laboratory settings, as well as in semiconductor manufacturing and high-purity vacuum processes. Capillary tube thermal mass flow controllers are particularly favored for their cost-effective solutions in gas flow control, featuring compact design, single penetration of the process line, and an integrated control system.
Principle of Operation
In capillary tube thermal mass flow meters, the flow splits into two internal paths. One path passes through a heated capillary sensor tube, while the other flows through a split-flow bypass. The ratio of flows through the bypass and sensor tube remains constant. The sensor tube measures mass flow rate based on the heat capacity of the gas, providing an accurate measurement. In a capillary tube thermal mass flow controller, an integrated flow control valve adjusts the mass flow rate to a user-set value.