Carbonating Beverages
Carbonation is a chemical process in which a liquid becomes saturated with carbon dioxide (CO2). Henry’s law, a fundamental physics principle, explains this thermodynamic phenomenon. It states that at a constant temperature, the amount of gas dissolved in a liquid is proportional to the pressure of the gas above the liquid. When it comes to carbonation, the goal is to achieve a specific concentration of CO2 in a liquid. It is essential to consider specific pressure and temperature conditions, depending on the type of product. Meticulous control of this equilibrium throughout the process is essential, and this is where flow control tools come into play.
Today, carbonated beverages are among the popular drinks and are used alongside various foods. The gas found in these beverages is mainly carbonic gas (CO2), also known as carbon dioxide. The primary purpose of adding carbonic gas to beverages is to enhance freshness and the lingering pleasant taste after consumption. Even the finest carbonated beverages lose their appeal when they lose their gas. There are two main reasons for adding CO2 to beverages: firstly, it serves as a preservative, preventing the growth of bacteria in the liquid during storage, and secondly, it is necessary for carbonation.
The quality of the added carbon dioxide gas to beverages is of great importance. The effervescence and tangy taste of carbonated drinks are due to the presence of carbonic gas in them. When carbonic gas mixes with a beverage, it creates a very weak acid called carbonic acid. It imparts a mildly tangy flavor. The level of this acidity is so low that it merely contributes to a pleasant sensation when consuming carbonated beverages. Furthermore, carbonic acid aids in food digestion in the gastrointestinal tract and is also perceived as a preservative in beverages. This is why well-known carbonated beverage manufacturers worldwide place great emphasis on the quality of the carbonic gas used in their beverages, and the consumable carbonic gas must meet specified criteria set by relevant experts.
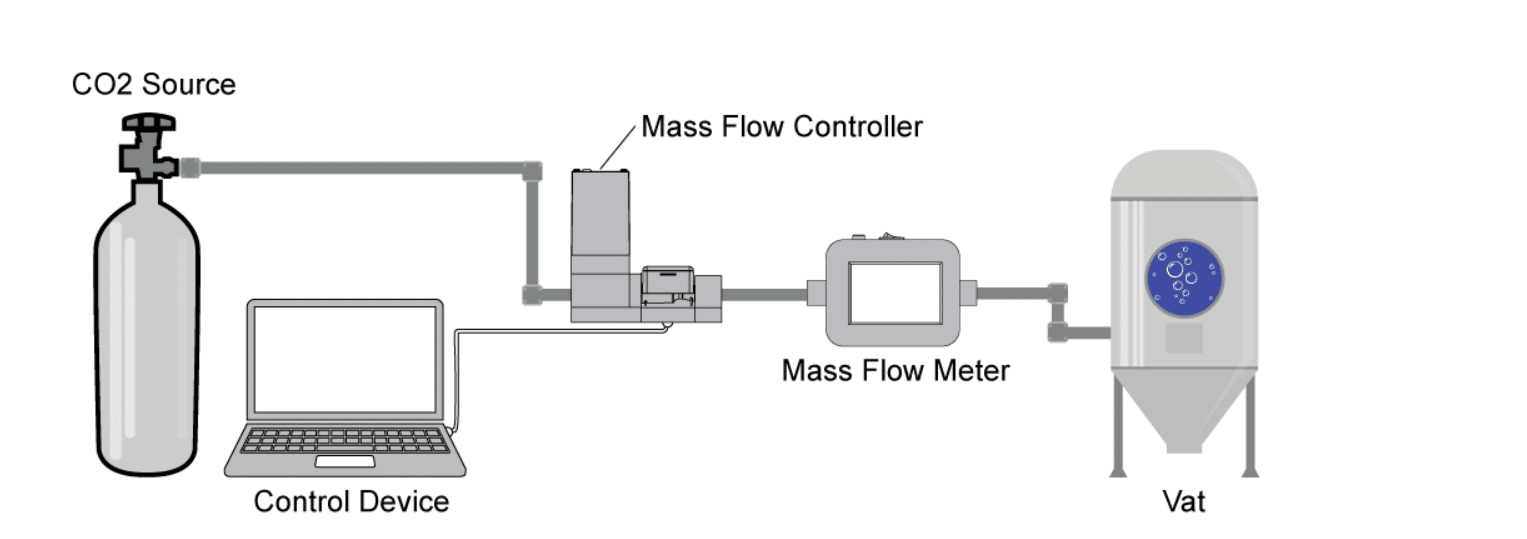

In the process of injecting CO2 gas, flow meters play a vital role. A thermal mass flow meter measures and controls the amount of carbon dioxide that dissolves in carbonated beverages during the carbonation process.
A thermal mass flow meter enables the accurate measurement and control of the flow rate of carbonated beverages. So, ensuring uniform and precise distribution or transfer of the beverage. This can contribute to maintaining product quality, reducing waste, and improving efficiency in the production or distribution process. In general, incorporating a thermal mass flow meter into the system of a carbonated beverage allows for better monitoring and control of flow rates, leading to improved accuracy and efficiency in handling the beverage.